-
 From the beaches of Normandy to Berlin
From the beaches of Normandy to BerlinHistory of D-Day and World War 2
Told by those who were there
What was the Second World War?
WWII stands as one of the darkest chapters in human history, marked by staggering casualties estimated between 50 to 85 million, with the toll falling heavily on civilians, particularly in the Soviet Union and China. The war inflicted unimaginable suffering, with millions falling victim to genocides, including the Holocaust, systematic starvation, massacres, and rampant disease.
Aircraft emerged as crucial assets in the conflict, playing pivotal roles in strategic bombing campaigns aimed at crippling enemy infrastructure and morale. Moreover, WWII witnessed landmark technological advancements, including the development and deployment of nuclear weapons. The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 not only brought a decisive end to the war but also ushered in the nuclear age, forever altering the course of human history.
When did World War II begin?
Nazi Germany's pretext for the invasion was based on unfounded claims of an imminent Polish attack, despite the absence of credible evidence. In reality, Poland had been actively engaged in diplomatic efforts to secure a non-aggression pact with Germany in the preceding months. The invasion itself was marked by unparalleled brutality, with Nazi forces inflicting unimaginable suffering on the Polish population. Over 6 million Polish civilians, including more than 2 million Jews, fell victim to Nazi violence, while the country's infrastructure was systematically destroyed.
In response to Germany's aggression, just two days later, on September 3rd, 1939, France and Britain declared war on Nazi Germany, officially signaling the commencement of World War II. The invasion of Poland served as a grim harbinger of Nazi Germany's willingness to resort to aggression and violence to achieve its objectives. Moreover, it precipitated a global conflict of unprecedented scale and destruction, leaving an enduring imprint on human history as one of the deadliest conflicts ever witnessed.
World War II casualties
Military deaths represent the sacrifices of soldiers and other armed forces personnel, while civilian deaths encompass the untold stories of non-combatants, including Jews, executed civilians, Roma and Sinti people, homosexuals, forced laborers, and countless others who fell victim to the atrocities of war. Let us never forget the profound sacrifices made during the Second World War, as we continue to learn from history and strive towards a future of peace and understanding.
What's new?
Recently added articles
This website is a labor of love and tribute to the veterans and victims of World War II. It is not motivated by politics or financial gain, and aims to provide comprehensive and accurate information about the war.
The most decisive battles of WW2
Adolf Hitler's rise to power
Adolf Hitler, born on April 20, 1889, in Braunau am Inn, Austria-Hungary, underwent a transformative journey that brought him to Germany in 1913. His experiences as a soldier in World War I profoundly influenced his political outlook, paving the way for his ascent to power.
The Deutsche Arbeiterpartei (DAP), founded on January 5, 1919, by Eckart, Anton Drexler, Gottfried Feder, and Karl Harrer, provided the platform for Hitler's political career. Joining the party in September 1919, Hitler quickly rose through the ranks, eclipsing Drexler's leadership with his charismatic oratory and radical vision. Under Hitler's direction, the DAP underwent a transformation into the Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei (NSDAP), or Nazi Party, adopting a 25-point program that articulated its nationalist and anti-Semitic agenda. By 1921, Hitler had assumed full control of the party, relegating Drexler to a marginal role.
The Nazy party increases its power
As Adolf Hitler assumed leadership of the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP), the party underwent a significant evolution, marked by a shift towards a more aggressive and ominous stance. This transformation was underscored by the establishment of the paramilitary Sturmabteilung (SA) in collaboration with Ernst Röhm, signaling a militarization of the party's approach.
The NSDAP strategically tapped into widespread public discontent stemming from various sources, including economic hardships, the lingering impact of the Treaty of Versailles following World War I, and the prevailing political instability in post-war Germany. By capitalizing on these grievances, Hitler sought to galvanize support for the NSDAP's radical agenda.
Moreover, the interplay of religious affiliations and regional sentiments played a significant role in shaping political dynamics, particularly in Bavaria. With its predominantly Catholic population, Bavaria harbored reservations against the central authority emanating from predominantly Protestant Berlin. Recognizing Bavaria's potential as a stronghold for his movement, Hitler targeted the region as a key battleground in his quest for power.
Mein Kampf
Hitler's strategic pivot post-Putsch focused on leveraging legal avenues rather than direct force to ascend to power. A central tenet of his ideological platform was the scapegoating and vilification of the Jewish population, which served as a unifying rallying cry for the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP). Rooted in social Darwinism, the NSDAP propagated the notion of Aryan racial superiority while advocating for the marginalization or eradication of perceived "inferior" races.
"Mein Kampf" served as a blueprint for Hitler's vision of German expansion, or "Lebensraum," alongside a comprehensive societal and economic overhaul. The systematic exclusion and persecution of Jews began in earnest following Hitler's rise to power in 1933. Legislative acts such as the infamous Nuremberg Race Laws of 1935 stripped Jews of their citizenship rights and imposed severe restrictions on their freedoms, including intermarriage and sexual relations with non-Jews.
From street fighters to political power
In the crucial parliamentary elections of 1930 and 1932, the Nazi Party experienced a remarkable surge in representation within the Reichstag, the German parliament. Although they fell short of securing an outright majority, their escalating influence marked a profound shift in the political landscape, positioning them as a potent force to be reckoned with.
The Weimar Republic, established in the aftermath of World War I, grappled with the daunting task of forming stable coalition governments amid a fractured political environment. Traditional parties struggled to effectively address the pressing economic and social challenges of the era, leaving room for more extreme ideologies to gain traction. Against this backdrop of uncertainty and unrest, influential conservative and business figures saw an opportunity to leverage the rising popularity of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party as a bulwark against the perceived threat of communism. Through clandestine negotiations, these power brokers sought to co-opt Hitler and his associates to stabilize the government and safeguard their own interests.
On January 30, 1933, President Paul von Hindenburg succumbed to pressure from conservative advisors and appointed Adolf Hitler as Chancellor of Germany. This decision, made in the hopes of harnessing Hitler's nationalist appeal within a broader coalition government, was driven by a belief that they could control and manipulate the Nazi Party for their own ends. However, this shortsighted strategy underestimated the fervor and ambition of Hitler and his followers, setting the stage for a seismic shift in German and global politics.
The burning of the Reichstag
However, in 1955, SA (Sturmabteilung) man Hans Martin Lennings made a notarially recorded statement challenging the official narrative. Lennings asserted that van der Lubbe could not have acted alone, claiming he had driven the Dutchman to the Reichstag by car. Upon their arrival, Lennings and his colleagues allegedly detected the smell of fire and observed light smoke, suggesting that the fire had already been initiated, possibly by the Nazis themselves, before van der Lubbe arrived.
The aftermath of the Reichstag Fire had profound consequences. On March 23, 1933, in response to the incident, the Nazi Party swiftly passed the Law for the Protection of the People and the State. This legislation granted the government sweeping powers to suppress opposition, marking a significant leap towards the Nazi Party's establishment of absolute control over the state. The law served as a pivotal moment in the erosion of civil liberties and the consolidation of authoritarian rule in Nazi Germany.
Dietrich Eckart

The origins of Nazism can be traced back to Dietrich Eckart.
Hitler's political manifesto

Adolf Hitler embarked on writing Mein Kampf while incarcerated after his unsuccessful coup in Munich. The book was published in two volumes in 1925 and 1926 respectively.
Hitler becomes Chancellor

Adolf Hitler and German President Paul von Hindenburg, pictured shortly after Hindenburg's invitation for Hitler to assume the position of chancellor in 1933.

Marinus van der Lubbe was a Dutch communist who gained infamy for his alleged role in the Reichstag Fire of February 27, 1933, in Berlin, Germany. Born on January 13, 1909, van der Lubbe became politically active during a period of intense social and economic upheaval in Europe.
The 'Kristallnacht'
In the wake of the expulsion of Polish citizens of Jewish descent residing in Germany, a pivotal moment unfolded when a 17-year-old named Herschel Grynszpan shot German diplomat Ernst vom Rath at the German embassy in Paris. This act was a direct response to the expulsion of Grynszpan's parents, who had called Germany home since 1911. Vom Rath succumbed to his injuries two days later, sparking tensions that led to hostility against the Jewish community within Germany.
The night of November 9 to November 10, 1938, marked a significant turning point as a notable anti-Jewish incident occurred. Termed Kristallnacht, or the "Night of Broken Glass," this episode earned its name from the fragments of shattered windows strewn across German streets. Synagogues, private homes, and businesses owned by Jewish individuals were targets of vandalism and looting that evening. Numerous buildings were set ablaze. The aftermath resulted in the apprehension and deportation of numerous Jews to concentration camps.
The 'Endlösung' or Final Solution
Known as the "Endlösung" or "Final Solution" for short, the National Socialists adopted this term in July 1941 to summarize their goal of systematically eliminating individuals they identified as Jews throughout Europe and beyond. This pursuit persisted until the Wehrmacht's unconditional surrender. The process began with the segregation of Jews in ghettos and culminated in the implementation of the Nazi policy labeled the "Final Solution to the Jewish Question."
This policy was worked out by Nazi officials during the Wannsee Conference in Berlin on January 20, 1942. Regrettably, this course of action led to the Holocaust, a tragic phase marked by the systematic and extensive extermination of European Jews.
The Holocaust history
The history and therefore the definition of the Holocaust also known as the Shoah (Hebrew) is exceptionally complex. Basically it can be stated that it was the murder or genocide of the European Jews during world war 2.
I made the visit deliberately, in order to be in position to give first-hand evidence of these things if ever, in the future, there develops a tendency to charge these allegations merely to “propaganda.””
Discover the history of the Nazi concentration camps

June 6 1944, D-Day Normandy
What was D-Day?
D-Day was the the Allied answer to occupancy and hostile regime of Nazi Germany with the end goal of putting an end to WW2. At 06:30 am on Tuesday June 6th, 1944 Operation Neptune or D-Day (amphibious assault) is unleashed along a 60 mile stretch of coast between the Cotentin Peninsula and the Orne River in Normandy, France. The invasion on the shores of Normandy were part of Operation Overlord (Allied invasion of Normandy).
Planning for D-Day
Planning for the operation began in 1943. Overlord was an Allied military operation of unprecedented scale, with an amphibious assault from Allied troops on the beaches combined with Allied airborne operations behind enemy lines inland. The Allies conducted a substantial military deception, codenamed Operation Bodyguard, to mislead the Germans as to the date and location of the main landings.
D-Day was originally planned for June 5
In the months leading up to the invasion, the weather was far from ideal and the operation had to be delayed 24 hours until June 6th, 1944. A further postponement would have meant a delay of at least two weeks, as the invasion planners had requirements for the phase of the moon, the tides, and the time of day that meant only a few days each month were deemed suitable.
The landings beaches in Normandy
The amphibious assault focused on five separate beaches in Normandy codenamed Omaha, Utah (American sector), Gold, Sword (British sector), and Juno (Canadian sector). At the end of the day small beachheads had been secured. It would turn out to be the turning point of World War 2 in western Europe.


Dodenherkdenking
The Netherlands celebrates it's liberation
Liberation Day (Dutch: Bevrijdingsdag) is celebrated each year in the Netherlands on 5 May to mark the end of the occupation by Nazi Germany during WW2. It follows the Remembrance of the Dead (Dodenherdenking) on 4 May. Holland was liberated by Canadian forces, British infantry divisions, British I Corps, 1st Polish Armoured Division, American, Belgian, Dutch and Czechoslovak troops. Parts of the country, in particular the south-east, were liberated by the British Second Army which included American and Polish airborne forces (see Operation Market Garden) and French airbornes (see Operation Amherst). On 5 May 1945 the Canadian General Charles Foulkes and the German Commander-in-Chief Johannes Blaskowitz reached an agreement on the capitulation of German forces in the Netherlands in Hotel de Wereld in Wageningen. One day later the capitulation document was signed in the auditorium of Wageningen University.

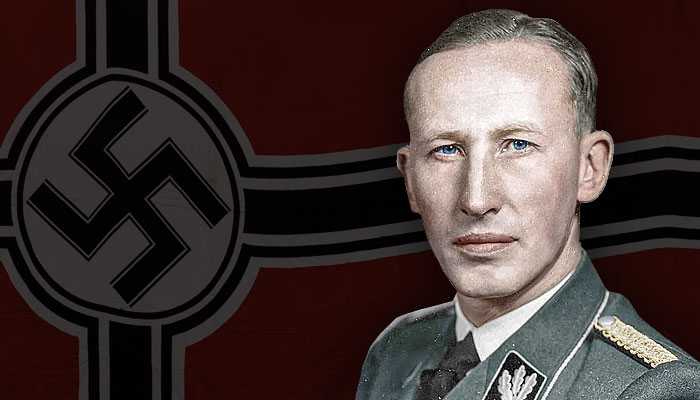
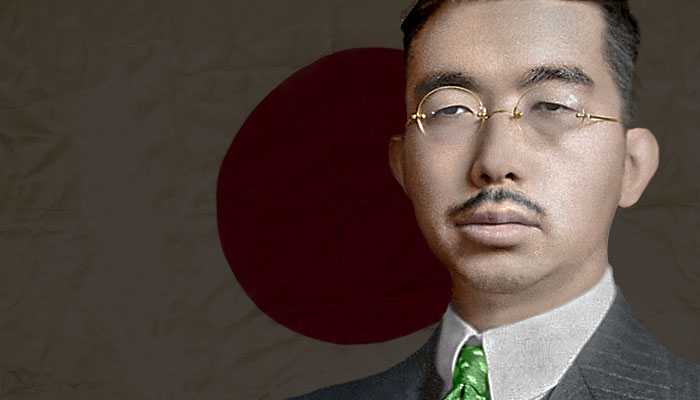
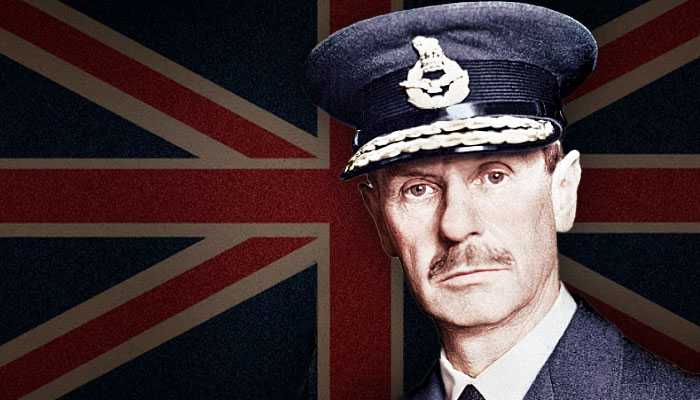
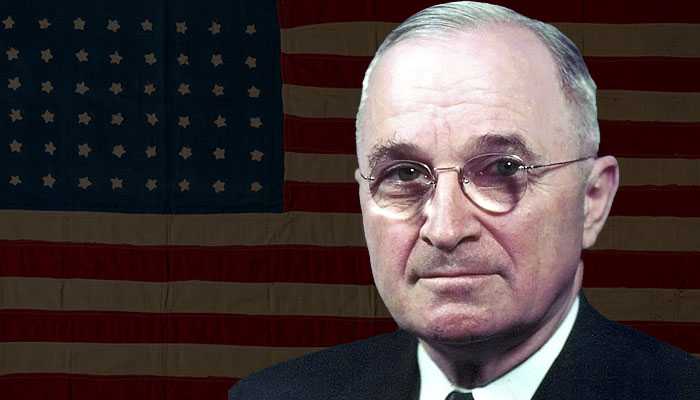
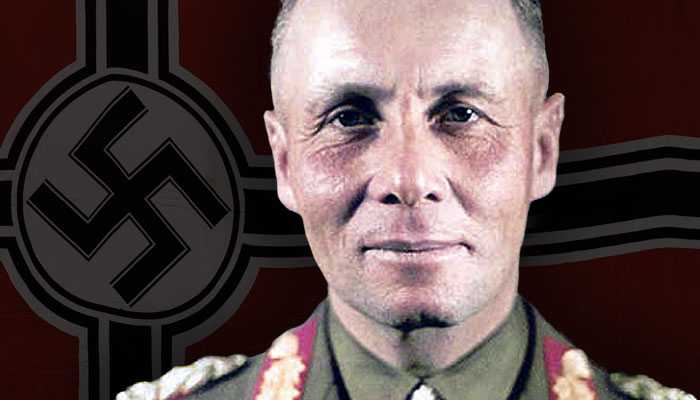
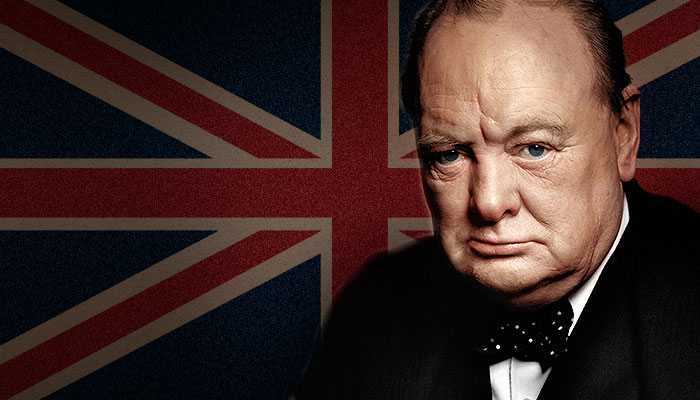
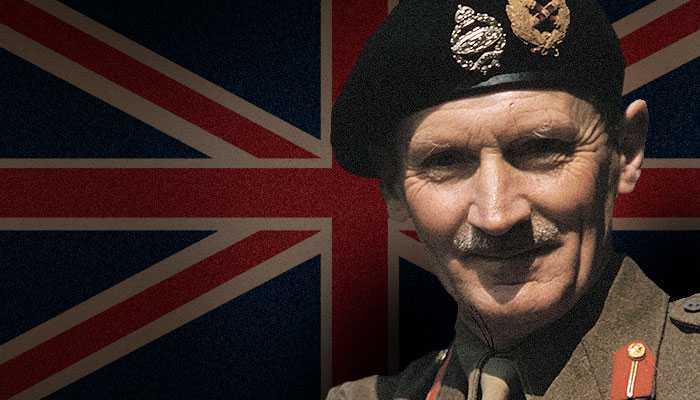
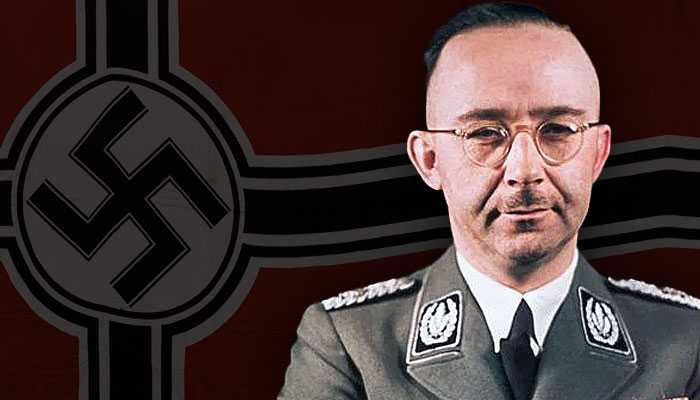
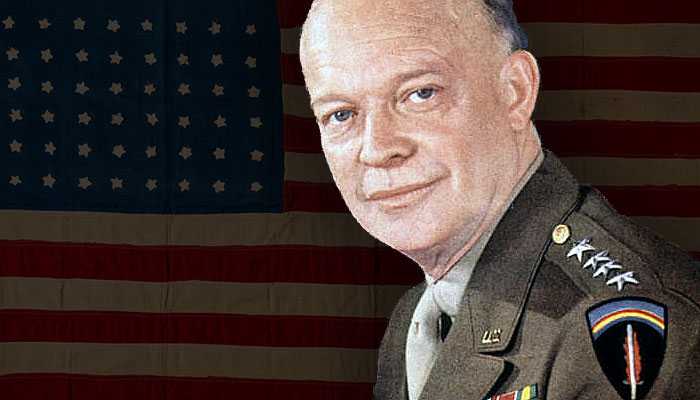
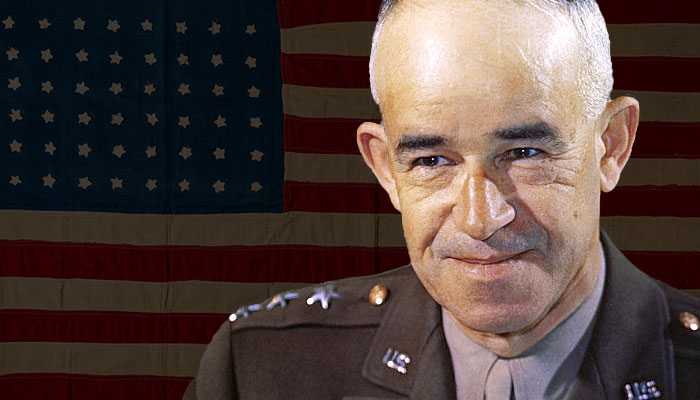
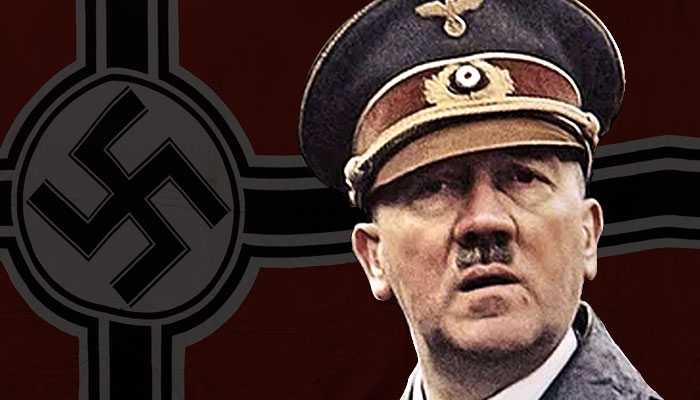
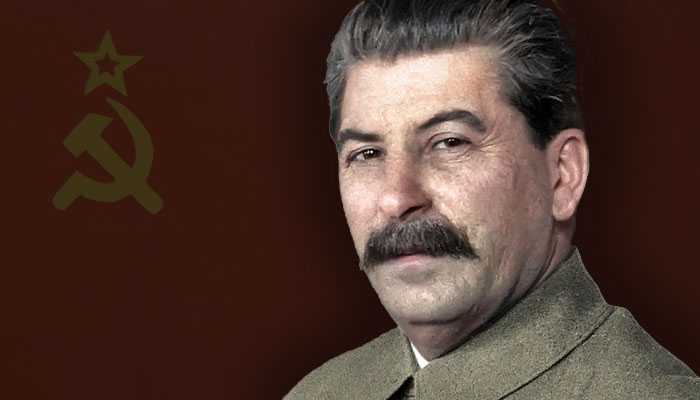
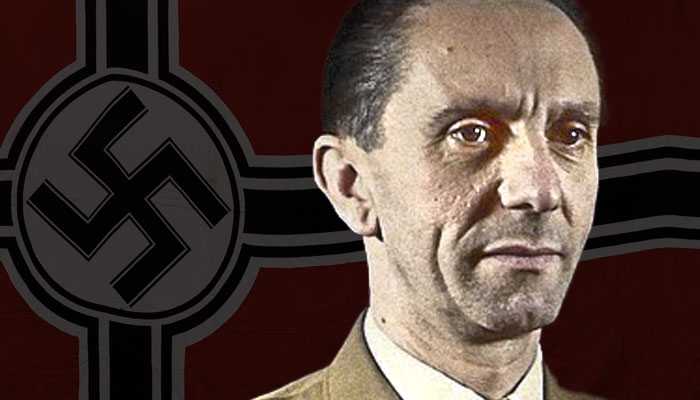
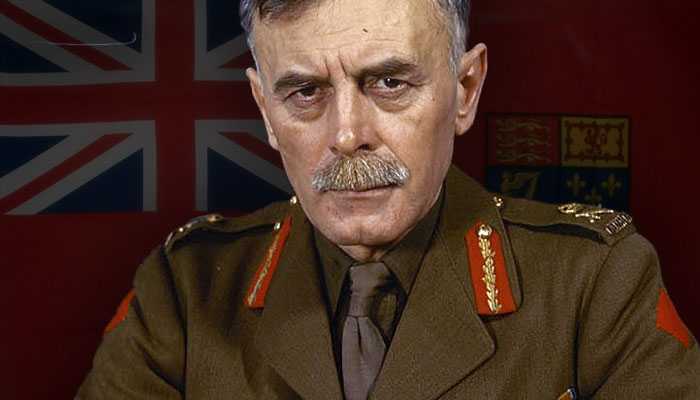
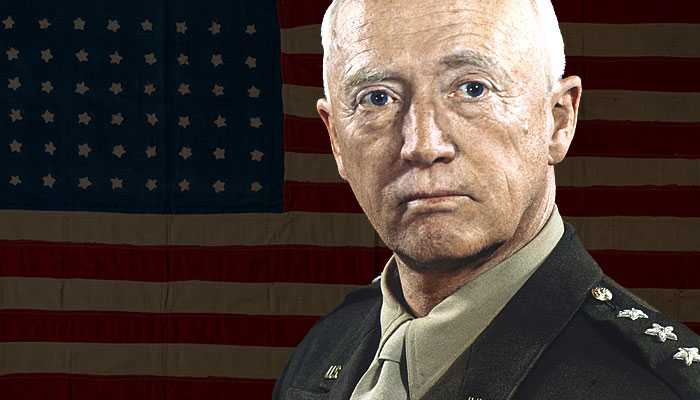
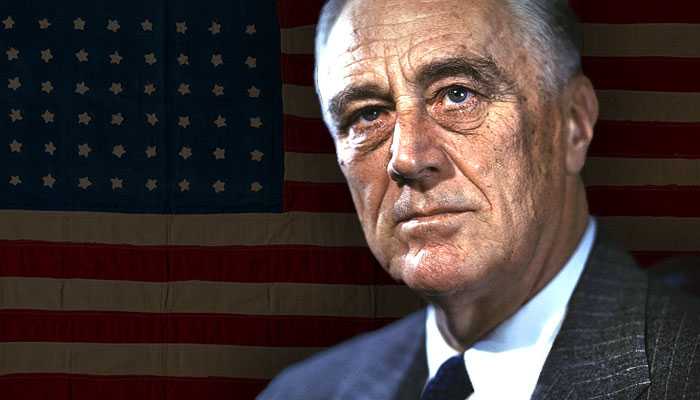
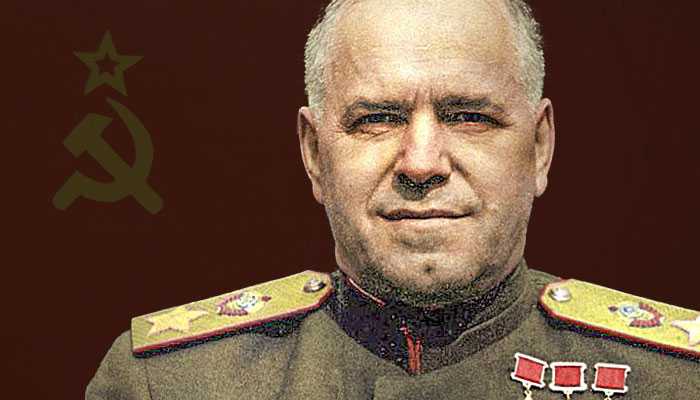
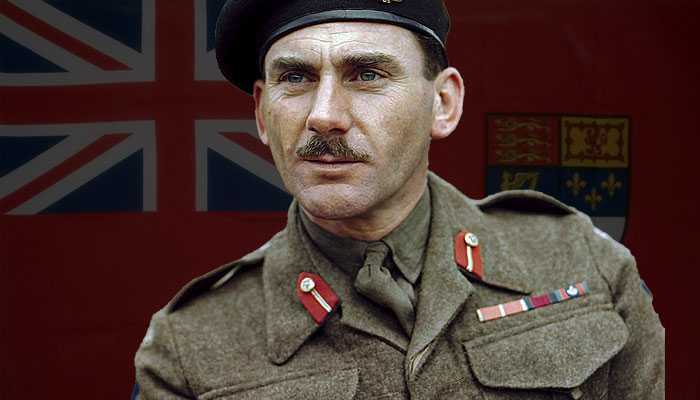
Leaders of the Axis and Allied forces during WW2
Another website about World War 2?
June 6th, 1944 (D-Day) was the starting point for this website back in 2000. This website is my personal 'one man' project and it started out based on the eyewitness accounts of the Allied and Axis troops of WW2 who fought on the beaches of Normandy during D-Day and in the Battle of Normandy. Over time and to be more complete, I added my focus on the Holocaust, concentration camps, aktion T4, the main battles without forgetting the war on the Eastern front, the Pacific and the rest of Europe. The historically accurate pages covering the complete WW2 history are made to educate readers about a conflict of this magnitude. This website can be used for education, personal interest as well as for research. I hope you take the time to explore my website. Thank you!